Evap Cooling VS Refrigerant Cooling
Choosing the right cooling system is essential for keeping your home comfortable and energy-efficient. Evaporative cooling and refrigerant cooling (air conditioning) each offer unique benefits, depending on your climate.
Evaporative Cooling vs. Refrigerant Cooling: Choosing the Right System for Your Home
When it comes to cooling your home, two of the most common options are evaporative cooling and refrigerant cooling (air conditioning). Each system has its own advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to choose the one that best suits your climate, budget, and cooling needs.
How Evaporative Cooling Works
Evaporative cooling uses water and airflow to cool the air. Warm outside air is drawn into the system and passed over water-soaked cooling pads. As the air moves through these pads, it absorbs moisture, reducing the temperature and increasing humidity. The cooled air is then distributed throughout the home.

Pros of Evaporative Cooling:
Energy Efficient – Uses less electricity, making it an eco-friendly cooling solution.
Fresh Air Circulation – Continuously brings in fresh air from outside rather than recirculating indoor air.
Environmentally Friendly – Uses water instead of refrigerant gases, reducing environmental impact.
Cons of Evaporative Cooling:
Less Effective in Humid Conditions – Since it adds moisture to the air, it works best in dry climates and loses efficiency in humid environments.
Requires Water Supply – Needs a consistent source of water to function properly.
Can Introduce Dust & Allergens – Brings in outside air, which may contain dust and allergens.
Limited Cooling Capacity – May struggle to effectively cool large spaces or homes in extreme heat.
How Refrigerant Cooling Works
Refrigerant cooling, commonly known as air conditioning, uses a refrigerant gas to absorb and remove heat from indoor air. The system compresses and expands the refrigerant, allowing it to cycle through indoor and outdoor units to cool the air. Unlike evaporative cooling, this method also dehumidifies the air, making it feel even cooler.
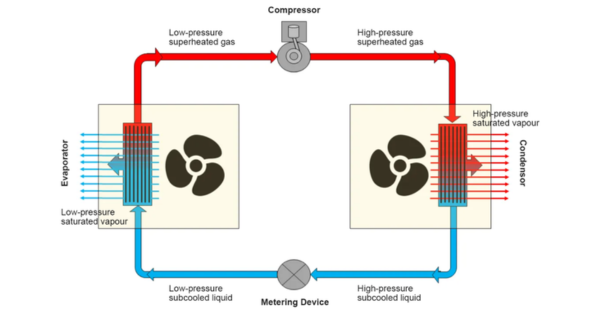
Pros of Refrigerant Cooling:
Powerful Cooling – Provides consistent and effective cooling, even in extreme heat and humid conditions.
Dehumidification – Reduces indoor humidity, preventing excess moisture buildup.
Suitable for All Climates – Works well in both dry and humid environments.
Precise Temperature Control – Allows users to set and maintain a specific indoor temperature.
Cons of Refrigerant Cooling:
Higher Cost – More expensive to install and operate than evaporative cooling.
Energy Consumption – Uses more electricity, which can increase energy bills.
Refrigerant Impact – If not properly managed, refrigerant gases can contribute to environmental concerns.
Recirculated Air – Relies on recycling indoor air, which may affect air quality and spread dust or odours.
Which Cooling System is Right for You?
Choosing between evaporative cooling and refrigerant cooling depends on your specific needs. If you live in a dry climate and want an energy-efficient, eco-friendly option, evaporative cooling may be ideal. However, if you need consistent cooling power, dehumidification, and climate versatility, a refrigerant-based air conditioning system is the better choice.
Final Thoughts
Both evaporative and refrigerant cooling systems offer unique benefits, but the best choice depends on your home’s climate and cooling needs. At Woodpecker, we offer expert advice on choosing the best cooling solution for your home. Contact us today to explore our range of evaporative and refrigerant cooling systems and find the perfect fit for your space.
